Simple explanation of Teradata Architecture
Teradata acts as a single data store, with multiple client applications making inquiries against it concurrently.
Instead of replicating a database for different purpose, with Teradata you store the data once and use it for all clients.
It provides the same connectivity for an entry-level system as it does for a massive enterprise data warehouse.
A Teradata system contains one or more nodes
A node is a term for a processing unit under the control of a single operating system.
The node is where the processing occurs for the Teradata Database there are 2 types of Teradata systems
Symmetric multiprocessing (SMP): An SMP Teradata system has a single node that contains multiple CPU’s sharing a memory pool.
Massively parallel processing (MPP): Multiple SMP nodes working together comprise a larger, MPP implementation of Teradata.
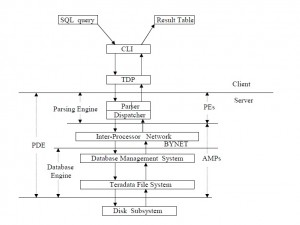
The nodes are connected using BYNET, which allows multiple virtual processors on multiple nodes to communicate with each other.
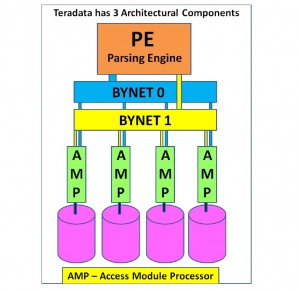
3 main components
Parsing Engine
BYNET
Access Module Processor
Learn more about Teradata Architecture in detail
2 thoughts on “Teradata Architecture”